Biofuels M&A: 2022 Review and Outlook
February 22, 2023 | By Bruce Comer, Frank Kim, and Zak Putlak
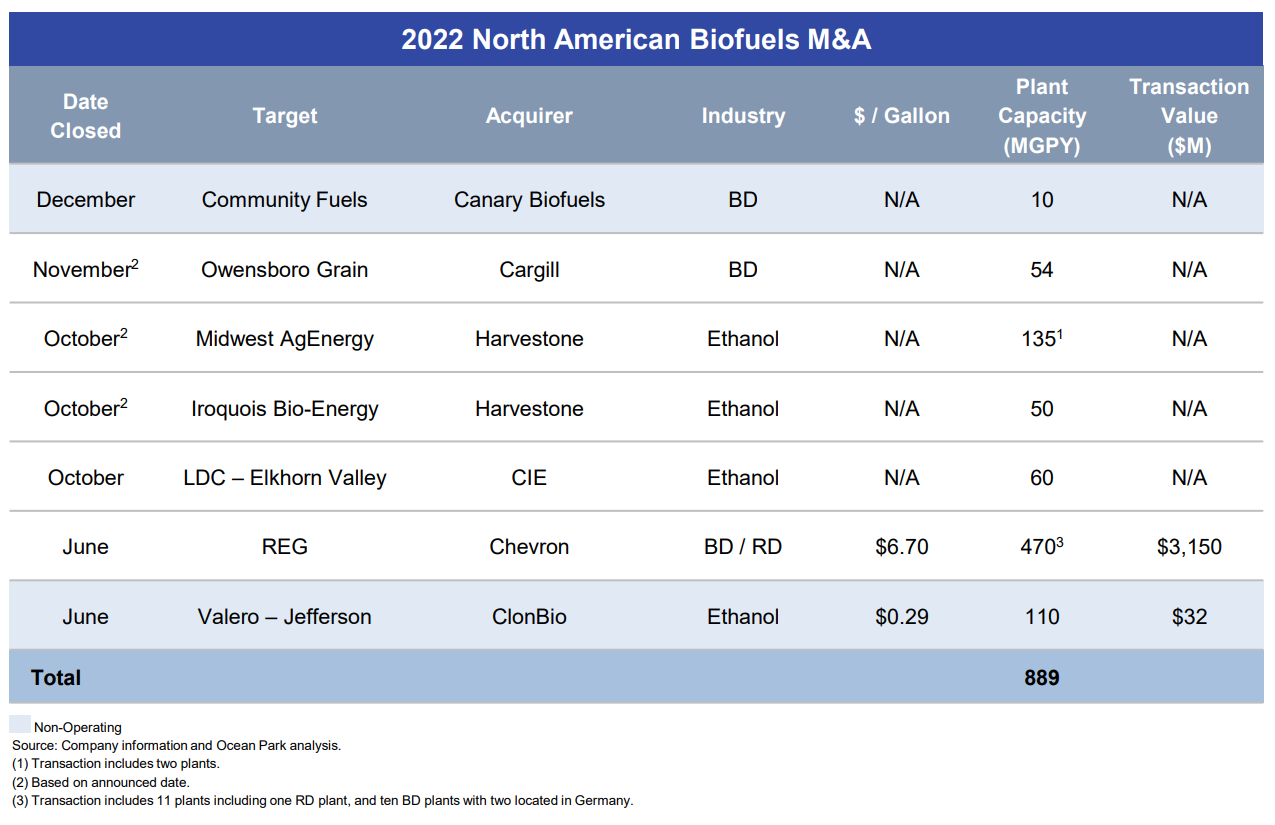
The market for buying and selling biofuels plants followed a historic 2021 with a transformational year in 2022, driven by one pivotal biomass-based diesel (BBD) transaction. Overall, seven mergers and acquisitions transactions took place, with 889 million gallons per year (MGPY) of capacity trading hands, the second highest in the past decade. Four of the seven transactions were in ethanol, involving five relatively small or non-operating plants with production capacity of 355 MGPY.
To be sure, beyond M&A, the sector attracted significant interest with billions of dollars of investment in renewable diesel (RD) construction, securing feedstock and carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) projects.
The significant BBD deal was Chevron’s $3.15B acquisition of REG, giving it a fleet of 11 refineries with total production capacity of 470 MGPY. This was the single largest BBD M&A transaction ever and marks the oil giant’s foray into BBD production as it decarbonizes its energy mix. With this acquisition, Chevron now controls 10% of US BBD production capacity, making it the third-largest producer. This transaction further concentrates biofuels production capacity — Valero, Chevron, and six other integrated producers now control 64% of BBD production capacity.
ETHANOL M&A
NORTH AMERICAN ETHANOL M&A, 2018-2022
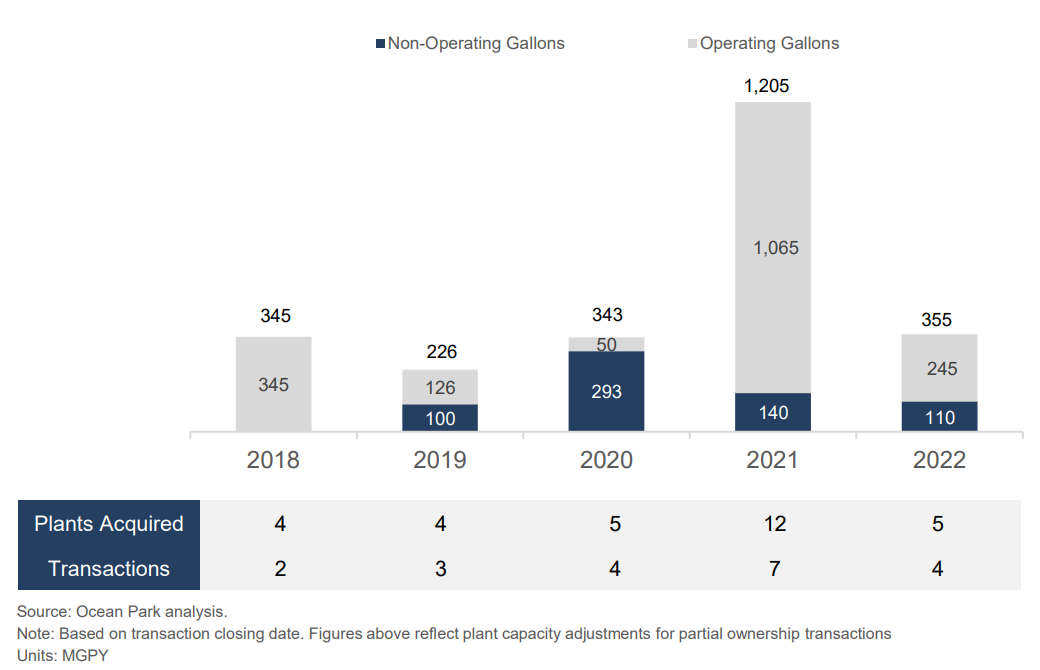
In 2022, ethanol M&A fell from a standout year in 2021 with seven deals involving 1.2 BGPY, nearly halving the deal flow. Of the five plants that were acquired, four were operating plants making up the majority of the capacity sold.
The four transactions involved five plants with 355 MGPY of combined capacity:
- Harvestone bought two ethanol plants from Midwest AgEnergy in North Dakota. Harvestone, a US based commodity merchant focused in the biofuels sector acquired two ethanol plants, Blue Flint and Dakota Spirit, in Underwood and Spiritwood, North Dakota. The two facilities have a combined nameplate capacity of 135 MGPY. Midwest AgEnergy had been part of Harvestone’s marketing and trading platform in 2020. With this transaction, Harvestone made its first ethanol plant acquisition(s) in the US.
- Harvestone acquired the interests of Iroquois Bio Energy Company in Rensselaer, Indiana. Harvestone acquired another operating ethanol plant, adding 50 MGPY to its total production capacity. Iroquois had been part of Harvestone’s marketing and trading platform since 2018.
- CIE acquired Louis Dreyfus Company’s Elkhorn Valley ethanol plant in Norfolk, Nebraska. CIE, an operating company of Chicago-based CC Industries and one of the largest producers of grain-based high-quality, specialty alcohols, acquired the 60 MGPY plant.
- ClonBio acquired Valero’s ethanol plant in Jefferson, Wisconsin. The idled 110 MGPY plant sold for $32M in June. The sale reduced Valero’s production capacity by approximately 6%. Valero previously acquired the plant in 2009 from Renew Energy in bankruptcy.
In parallel to M&A, ethanol producers in 2022 announced and invested billions in decarbonization and the development of co-products, including sustainable aviation fuel, high protein feed and enhanced corn oil recovery which can be used as a feedstock for RD. The 45Q tax credit, originally passed in 2008, continued to spur investment in CCS projects. The passage of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) last summer further increased the potential value of the 45Q credit and introduced the 45Z tax credit. Ocean Park tracked 11 notable CCS announcements during the year.
2022 MAJOR CCS ANNOUNCEMENTS
US ethanol producers are betting heavily on carbon capture and storage technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and profit from the IRA’s policy incentives. Two major pipelines for carbon sequestration are under development while other producers have established on-site injection projects.
Pipeline Announcements:
- Navigator will provide CCS services to POET that will involve five million metric tons of CO2 annually from 18 plants in Iowa, Nebraska and South Dakota by 2025.
- Navigator will provide CCS services to Big River that will involve one million metric tons of CO2 annually from three plants in Iowa by 2025 for 20 years.
- Navigator and Siouxland Ethanol reached a deal for Navigator to capture, transport and store up to 235 thousand metric tons of CO2 annually in Jackson, Nebraska.
- Vault CCS Holdings received a controlling investment from Grey Rock Investment Partners to continue developing its carbon pipeline throughout the Midwest and Canada.
- Tallgrass will transport CO2 from ADM’s Columbus plant via the repurposed Trailblazer natural gas pipeline and sequester it in Eastern Wyoming.
- ADM partnered with Wolf Carbon Solutions to decarbonize its Clinton and Cedar Rapids, Iowa ethanol plants through a newly constructed pipeline to be stored underground at ADM’s fully permitted and already operational site in Decatur, Illinois.
- Summit Carbon Solutions secured agreements for more than half of the proposed pipeline route in November. The project has commitments from 30+ ethanol facilities to capture and permanently store the carbon in North Dakota.
On-Site Injection Announcements:
- After six years of R&D, Red Trail Energy sequestered carbon at its ethanol facility located near Richardton, North Dakota in June.
- Carbon America partnered with Sterling and Yuma Ethanol to capture and store up to 95% of emissions per year.
- Carbon America announced an agreement with Bridgeport Ethanol in which it will finance, build, own and operate the CCS system at Bridgeport’s plant.
- Marquis announced plans for the Marquis Industrial Complex to be the world’s first carbon-neutral industrial complex that has access to on-site carbon injection.
BIODIESEL & RENEWABLE DIESEL M&A
NORTH AMERICAN BIODIESEL & RENEWABLE DIESEL M&A, 2018-2022
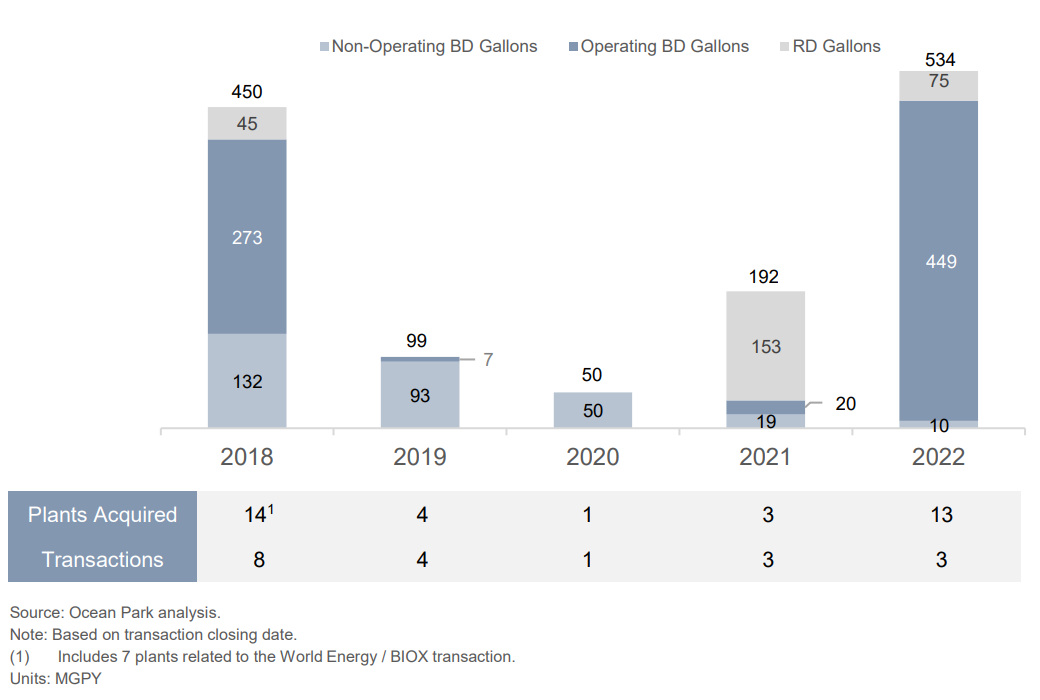
Biodiesel (BD) and renewable diesel M&A was standout in 2022 due to Chevron’s acquisition of REG. The only RD plant to trade was included in the REG deal. Other than the landmark transaction, deals were limited.
Rather than buying plants, the story in BBD has been RD construction and feedstock investments. For instance, Cargill’s takeover of Owensboro Grain was driven by Cargill’s efforts to expand its soybean processing capabilities. Meanwhile, integrated refiners continued their spending spree in RD to build and retrofit plants.
There were three BBD M&A transactions in 2022, totaling a transfer of 534 MGPY capacity.
- The headliner was Chevron’s Acquisition of Renewable Energy Group (REG). Chevron acquired all the outstanding shares of REG in an all-cash transaction valued at $3.15B. Prior to the transaction, Chevron did not own any biodiesel or renewable diesel plants, but it has pledged to invest $10B through 2028 in biofuels and other low-carbon energies. The deal fetched more than three times the highest dollar-per-gallon of nameplate capacity multiple than the previous highest on record at $6.70. Chevron paid a high price to position itself as a leader in BBD production and distribution, as well as feedstock collection. The acquisition of the largest US BD producer came with 10 BD plants, including two plants in Germany, along with one RD plant in Geismar, Louisiana which is currently being expanded by 250 MGPY. The acquisition will allow Chevron to fulfill its promise of producing 100,000 barrels per day of renewable fuels by 2030.
- Canary Biofuels acquired the assets of Community Fuels in California. Canary acquired the assets of Community Fuels, including a non-operating 10 MGPY BD plant and a fuel terminal in the Port of Stockton, California. The transaction is Canary’s second BD plant acquisition in the last two years and brings its total capacity to 30 MGPY.
- Cargill acquired Owensboro Grain Company in Owensboro, Kentucky. The Minnesota-based agribusiness giant acquired one of the few remaining independent soybean crush plants. With the acquisition, Cargill added 39.5M bushels of soy crushing capacity. In a feedstock-constrained world, Cargill quickly added more soybean oil to its offering. The purchase included a 54 MGPY BD plant and makes Cargill the second largest US BD producer by capacity.
In BBD, companies were largely focused on RD construction and securing feedstock. Over a billion gallons of RD capacity came online this year with another 980 MGPY planned for 2023, accounting for over $5B in investment through 2023. The rapid growth in RD capacity has spurred investments, joint ventures, and acquisitions aimed at securing feedstock supplies.
2022 MAJOR RD CONSTRUCTION ANNOUNCEMENTS
Internal investments in RD production capacity have displaced some of the BD/RD M&A activity. Eighteen plants with 4.8 BGPY of capacity are operating or expect to operate by 2024. The major announcements this year were:
- Cargill and Love’s began the construction of a new 80 MGPY plant in Hastings, Nebraska that will operate by mid-2024. The project is estimated to be worth $600M.
- New Rise Renewables Reno started up its 44 MGPY plant near Reno, Nevada. Phillips 66 will supply the feedstock and purchase 100% of the RD.
- Phillips 66 began the construction of a 680 MGPY expansion in Rodeo, California that will come online in 2024. The total cost of the conversion is approximately $850M.
- CVR Energy completed the conversion of its refinery in Wynnewood, Oklahoma into a 100 MGPY RD facility and commenced operations.
- Marathon and Neste formed Martinez Renewables, a 50/50 joint venture to produce RD at Marathon’s refinery in Martinez, California. The first phase of the project will see 260 MGPY of capacity come online in early 2023, followed by an additional 470 MGPY by the end of 2023.
2022 MAJOR RD FEEDSTOCK ANNOUNCEMENTS
The recent boom in RD production has tightened feedstock supply. This scarcity of feedstock has made its procurement and control over supply as important as owning biorefineries. Ocean Park is tracking 6.9B pounds of additional soybean oil to hit the market through 2026, enough to produce 900 MGPY of RD. There has also been numerous feedstock deals by RD producers and soy crush players ranging from capital for soy crush, acquisition of aggregators, joint ventures and M&A. Key feedstock deals include:
- Bayer increased its investment in oilseed producer CoverCress in a majority ownership deal with Bunge and Chevron. Earlier in the year, Chevron and Bunge partnered with CoverCress through their joint venture to secure a predictable supply of feedstock.
- ADM and Marathon broke ground on North Dakota’s first dedicated soybean processing facility through their JV, Green Bison Soy Processing. The JV is expected to produce 600 million pounds of refined vegetable oil which will be supplied exclusively to Marathon.
- ECP, a private equity investor focused on sustainability, acquired Goldman Sachs’ interest in Restaurant Technologies, one of the largest providers of cooking oils to increase its supply of low CI feedstock for its renewable fuel businesses.
- Martinez Renewables’ feedstock pretreatment is expected to come online during the second half of 2023 at Marathon’s converted RD facility in Martinez, California.
- Cargill acquired Owensboro Grain Company, a fully integrated soy processor. The acquisition brings additional feedstock supply under Cargill’s control.
- Neste acquired SeQuential, a used cooking oil collection and aggregation business in Oregon from Crimson Renewable Energy Holdings. The transaction boosts feedstock control on the west coast for Martinez Renewables.
NORTH AMERICAN BIOFUELS OUTLOOK FOR 2023
Regulatory: The highly anticipated EPA proposed ruling governing the next three years of biofuel mandates under the Federal Renewable Fuels Standard was unveiled in December. The proposal increases mandates to 22.68B gallons in 2025 from 20.63B gallons in 2022. Importantly, the Advanced Biofuel RVO component is growing at a much lower rate than projected RD capacity. Notably, obligated parties are increasingly internalizing their RVO compliance. By 2024, Ocean Park expects obligated parties to have the capacity to fulfill all of their Advanced Biofuels RVO.
The $737B IRA provides significant financial incentives dedicated to clean fuels, including $500M for biofuels infrastructure. Notably, the IRA extended the federal biomass-based diesel blending tax credit (BTC) to Dec. 31, 2024, which was set to expire at the end of 2022. Blending credits will be replaced from 2025-2027 by a clean fuel production credit that incentivizes reduction in carbon intensity (CI) with ethanol, BD, RD, and SAF all eligible for the credit. The program could be extended similarly to the BTC. The credit mostly applies to blending BD and RD (up to $1.00/gal), but SAF is eligible for the credit as well (up to $1.75/gal). The IRA also expanded the 45Q credit for carbon storage from $50/MT to $85/MT with five years of direct pay for projects that begin construction before January 1, 2033, making CCS economically viable for ethanol plants.
Ethanol: In 2022, ethanol producers saw profits dip from the highs of the fourth quarter of calendar year 2021. Conversely, future margin opportunity incentives provided by the IRA, coupled with pressures to spend substantial dollars on capex improvements to harvest these benefits, could be a catalyst for future ethanol M&A. Well-capitalized leading producers focused on product diversification and carbon strategies may be able to stave off low margins and take advantage of IRA and M&A opportunities.
BBD: Renewable diesel production soared 72% to 1.5B gallons in 2022 while biodiesel production declined by 5%. The obligated parties, primarily the domestic oil refiners, dominate RD production. One consequence of this expansion in RD, and BBD overall, has been surging feedstock prices. This has put pressure on smaller producers that are not integrated with distribution. Ocean Park expects RD production to continue ramping up in 2023, displacing imported BBD fuels and putting pressure on less efficient BBD producers. Only a few sizable, non-integrated independent BD producers remain. We expect M&A in RD and BD to be limited in 2023. However, industry dynamics will continue to put a premium on feedstock sources, driving investment and acquisition.
CONCLUSION
Biofuels M&A activity in 2022 again beat historical levels, and the market might continue to outperform the trend in 2023 if more ethanol plants go on the market. Significant announcements and investments made into RD construction and the land grab for BBD feedstock by refiners and the decarbonization of ethanol demonstrate increased interest in biofuels. If 2022 is any indication, traditional and renewable fuels industries will continue to converge.
ABOUT THE AUTHORS
 BRUCE COMER Managing Director (310) 670-2721 bruce@oceanpk.com |
 FRANK KIM Director (310) 670-7911 fkim@oceanpk.com |
 ZAK PUTLAK Associate (310) 670-2595 zputlak@oceanpk.com |
Ocean Park is a leading boutique investment bank focused on the renewable fuels, energy, food, AgTech and agribusiness sectors. The Ocean Park team has significant operational and transaction experience, including advising on mergers and acquisitions, financings and restructurings. Since its founding in 2004, Ocean Park has successfully completed over 80 transactions and client engagements, including over 35 biofuels transactions. Its professionals are based in Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston, Minneapolis, and Omaha.
This material is solely for informational purposes. The information in this document does not constitute an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to purchase, any security or to provide any investment advice.
Any securities are offered through Ocean Park Securities, LLC, a member of FINRA and SIPC. Ocean Park’s professionals are licensed registered representatives of Ocean Park Securities, LLC. For more information, please visit oceanpk.com or call (310) 670-2093.

